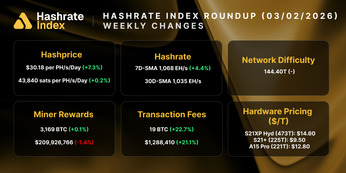
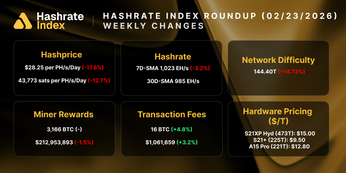
Hashrate Derivatives Monthly Lookback - August 2024
We are excited to introduce Luxor’s Derivatives Monthly Lookback Series: a monthly market deep dive into hashrate forward market activity. As hashrate markets mature and become increasingly sophisticated, our goal is to ensure that Bitcoin miners are equipped with the knowledge and tools they need to effectively manage their operations and investments.
In this inaugural post, we will cover August 2024’s hashrate market and hashprice trends, derivatives market participation and trading activity, and contract performance for the USD-denominated 1-month August 2024 hashrate forward contracts.
August 2024 Hashprice & Its Constituents
The mining industry recently saw its lowest USD and BTC-denominated hashprice month since 2017, with a notable plummet to a new all-time low. On August 5, Bitcoin miners faced a perfect storm: a global asset sell-off causing a steep decline in spot bitcoin price, a significant and unexpected mid-summer increase in network difficulty, and a stagnant transaction fee market. Daily USD hashprice bottomed at $37.70 PH/s/Day on the day.
USD Hashprice averaged $43.54 throughout August, beginning at $45.47 and falling to $42.19 by the end of the month. This trend was driven primarily by a falling spot Bitcoin price in conjunction with an all-time high in network difficulty and low transaction fees. Overall, BTC-denominated hashprice averaged 0.0007246 throughout August, beginning at 0.0007090 and slightly rising to 0.0007141 by the end of the month.
The average spot Bitcoin price in August was $60,063, down by 4.15% from $62,665 in July. A sharp 23.26% drop occurred from $66,100 on July 31 to $50,725 by August 5, driven by worsening U.S. labor market conditions, the unwinding of the Japanese Yen carry trade following a Bank of Japan rate hike, and rising geopolitical tensions. These factors persisted, leading to a Bitcoin price of $59,087 at the end of August, 7.86% lower than $64,125 at the start of the month.
Network difficulty saw a sharp 10.5% increase on July 31, reaching a record high of 90.67T. It briefly dropped 4.2% to 86.87T in mid-August before rising again 3.0% to 89.47T on August 28. The initial spike was unexpected, partly due to Texas' high electricity demand and 4CP high watermark in early July, allowing Miners to hash more than anticipated during the rest of month.
Average transaction fees throughout the month were the lowest since April 2022, averaging 0.0797BTC per block per day. However, on August 22, fees temporarily exploded during the launch of the Babylon staking protocol, with blocks reaching up to 15 BTC in rewards. Hashprice surged up to a local peak of ~$49.25/PH/Day.
Bitcoin miners collected an average of 0.15 BTC per block per day in transaction fees throughout that week, compared to the prior week's 0.06 BTC. In contrast, miners collected an average of 0.0506 BTC per block per day in the following week after the Babylon launch - a whopping 66.60% decline - as the craze calmed down. Although short-lived, this was a welcome surprise in week-to-week profitability for hashing miners.
On the whole, transaction fees constituted 2.43% of the block subsidy throughout the month. Had it not been for the Babylon boon, this proportion would have been 1.86%. This event highlights occasional speculative opportunities arising from asymmetric information about key developments in the Bitcoin ecosystem.
In terms of hashprice volatility, the month of August saw a rise amplified by the launch of the Babylon Protocol. From a year-to-date perspective, volatility throughout August was lower than in January and April–June, but in line with February through March.
The figure below summarizes overall hashprice & constituent activity throughout the month, highlighting key daily values:
August 2024 Forward Market Activity
Our analysis of the August forward hashrate market focuses on two key points: how the August 2024 hashrate contract traded in previous months and how the forward curve shifted in August based on trades for forward hashrate during the month.
The table below shows the evolution of Bitcoin hashrate forward markets throughout March - August 2024. Rows represent specific monthly contracts, while columns represent each trading month. Cell values indicate the average monthly mid-market price, except for the bold highlighted main diagonal, which shows actual hashprice settlement in each month. This table summarizes both the trading history of the August 2024 contract (colored row) and the forward curve in August (colored column).
Observing the colored row (Aug 2024), we can see how the August 2024 contract traded leading up to August compared to the actual hashprice settlement in each previous month. Given these values, we can make observations around how a specific contract would have performed relative to when it was traded, in addition to how a specific strategy of trading contracts (e.g., a 6-month rolling vs. 1-month rolling) would have performed versus spot hashprice. Finally, the bold highlighted main diagonal (i.e., actual monthly hashprice settlement values) shows how the shape of the forward curve changes throughout the months versus spot hashprice (trading in backwardation for this instance).
How August 2024 Hashrate Traded
The August 2024 contract was traded by a very diverse set of market participants. The primary sellers of both the deliverable (DF) and non-deliverable (NDF) August 2024 hashrate forward contract were private mining companies, as well as lenders and market makers. Private mining miners were selling the NDF to hedge their revenue and selling the DF to finance upgrades in newer generation hardware.
Lenders on the other hand, were using the NDF to lock in a yield on DF purchases with upfront payment. We see the discount of DF’s relative to NDF’s as the interest rate in hashrate-based lending markets. Buyers and sellers of the DF with upfront payment can use the NDF to lock-in a fixed yield or cost of capital, instead of having exposure to the uncertain and variable returns of hashprice. In August 2024, that yield or cost of capital was in the 10-13% annualized range.
Buyers of deliverable and non-deliverable August 2024 hashrate forwards involved all types of industry players: public and private miners as well as prop traders bought these contracts to temporarily increase their hashrate exposure.
Although hashprice ended up at all time lows in August 2024, it was not anticipated by the market ahead of time. Consequently, miners that hedged production had significantly higher revenues compared to unhedged miners. Miners who sold August hashrate in March (when the contract was first listed) earned on average $59.42 per PH/s/Day vs. $43.54 on a typical mining pool.
In other words, the further out a miner sold August 2024 hashrate, the more Bitcoin they mined.
In terms of revenue impacts, the figure below summarizes how a 1 EH mining operation would have performed, had it sold August 2024 hashrate forward versus during the month.
Public mining companies were not selling hashrate forward for August – an unfavorable position to be in as hashprice hit all time lows. The figure below illustrates a hypothetical scenario of how public miners' August production would have differed if they had hedged in March 2024 before the halving:
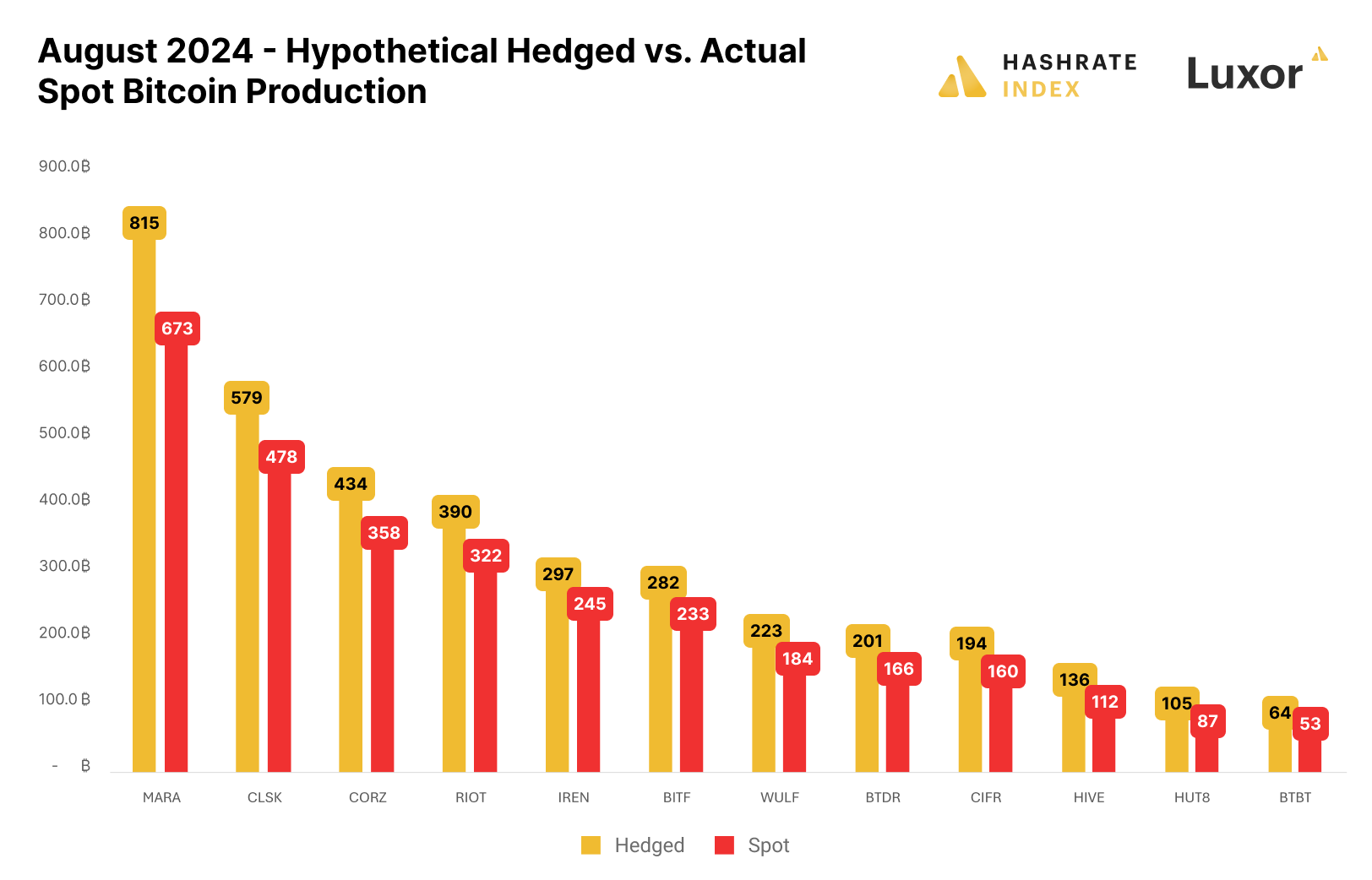
Please note: this figure is strictly for demonstration purposes and based on the simplifying assumption of multiplying actual production figures by the percentage difference between hashrate forward contracts’ locked-in hashprice versus spot hashprice; it excludes fees and bid/ask spreads associated with entering into hashrate forward contracts.
A second caveat: although selling forward proved to be favorable in this instance, it is critical to recognize that hedging is typically a cost of business rather than a revenue generation method. Hedgers willingly pay a price to buy certainty and obtain more predictable cash flows, which increases valuation, reduces cost of capital, and ultimately attracts investments.
How Forward Hashrate Traded in August 2024
During the month of August itself, the set of participants was a little less diverse – the industry was in a “wait and see” mode given that hashprice was at all-time lows. The sell side was predominantly private miners looking to lock-in hashprice, either to protect margins or to borrow and temporarily expand hashrate. On the other hand, the buy side consisted of private miners and speculators looking to profit on a rebound from all-time low hashprice.
The table below summarizes the evolution of Bitcoin hashrate forward markets during August 2024, for the subsequent five months from September 2024 through January 2025. Rows represent specific monthly hashrate contracts, while columns represent each trading month. Cell values indicate the average weekly mid-market price.
Observing each column, we can understand how the shape of the forward curve evolved throughout August and what the market expects going forward. For example, the September 2024 contract began trading in contango at the start of August and eventually ended up in backwardation as block times sped up. In fact, all contracts bottomed towards the beginning of the month and moved up towards the end. The front month spent most of August trading in contango but eventually turned into backwardation as the market priced in a lack of staying power for the sudden burst in transaction fees caused by Babylon.
Looking Ahead and Concluding Thoughts
Looking forward, both USD and BTC contracts are currently trading in backwardation throughout September 2024 - February 2025. Miners may lock in a ~$40 hashprice for up to six months into the future. Our derivatives desk is currently seeing upfront payments and financing deals through the DF at a 10-13% (annualized) discount to the NDF curve.
In summary, selling August 2024 hashrate forward prior to the month of August proved to be profitable for miners hedging their production. In addition, the further out a miner hedged the better their performance was.
As hashprice continues to hover around all-time lows, miners may consider a couple of cases for selling forward. First, that hashprice can always go even lower. For example, a significant decline in Bitcoin price could drive hashprice down to the $20's range, and in such a situation, hedging may save a miner from shutting down whereas unhedged miners would be risking their business. Second, although miners are earning an all-time low per hash, newer generation ASICs are not earning an all-time low per unit of electricity (i.e., on a kWh basis). Even at all time lows, there is meaningful margin for newer generation ASIC operators to lock in.
On the other hand, buy side participants may find the current hashprice environment to be an attractive entry point. Alternatively, miners tied to a hashcost above the forward curve (e.g., due to outdated ASICs or high electricity costs) can buy hashrate forward and immediately reduce their cost to acquire Bitcoin.
As we come to a close, we would reiterate that although outcomes from locking in hashprice may vary in or out of favor over time, hedging is meant to be a risk management tool. As the industry continues to mature, miners who choose to embrace the hedging and financing instruments made available to them may benefit from smoother cash flows, lower capital costs, and a sentiment of higher confidence from investors.
Building on Luxor’s derivative product suite - including exchange-traded Hashrate Futures and our recent announcement of expanded hashrate forward contract tenors up to 12 months - we look forward to strengthening our delivery of high-quality insights to support the Bitcoin mining industry.
If you’d like to learn more about Luxor’s Bitcoin mining derivatives, please reach out to [email protected] or visit https://www.luxor.tech/derivatives.
Disclaimer
This content is for informational purposes only, you should not construe any such information or other material as legal, investment, financial, or other advice. Nothing contained in our content constitutes a solicitation, recommendation, endorsement, or offer by Luxor or any of Luxor’s employees to buy or sell any derivatives or other financial instruments in this or in any other jurisdiction in which such solicitation or offer would be unlawful under the derivatives laws of such jurisdiction.
There are risks associated with trading derivatives. Trading in derivatives involves risk of loss, loss of principal is possible.
Hashrate Index Newsletter
Join the newsletter to receive the latest updates in your inbox.